Explain Different Types of Gsm Channels
Besides the TDMA in the GSMDCS we have also the FDMA technique. Traffic channels TCHs control channels CCHs and the cell broadcast channel CBCH.

Write A Note On Gsm Channel Types
GSM networks operate in a number of different carrier frequency ranges separated into GSM frequency ranges for 2G and UMTS frequency bands for 3G with most 2G GSM networks operating in the 900 MHz or 1800 MHz bands.

. As shown in the figure there are two main types of channels in the GSM. GSMDCS is characterised by a hybrid access to the channel. GSM owns a market share of more than 70 percent of the worlds digital cellular subscribers.
212 Explain Traffic Channels TCH Control Channels CCH in GSM. Reverse Channels The Reverse CDMA channel is the mobile-to-cell direction of communication or the uplink path. These functions and interfaces are explained in this chapter.
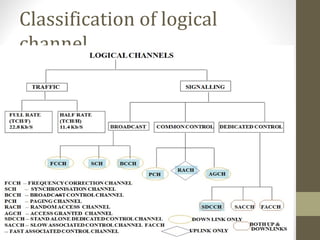
In GSM logical channels see Figure 74 are used to carry traffic and control information. There are two main categories here Full rate 13 kpbs and Half rate. It is for down-link only.
The designs of different antennas generate dissimilar radiation patterns and their complexity mainly depends on the design of an antenna. Explain the protocol architecture in GSM 12. Full rate traffic channels at a net bit rate of 228 Kbs TCHF Half rate traffic channels at a net bit rate of 114 Kbs TCHH.
BCH Broadcast Channel. A channel has two frequencies 80 MHz apart. A broad lattice of GSM channel types is explained.
As we saw in the post on the architecture of a mobile communication system a handoff otherwise known as a handover is a technique employed to maintain connectivity even when a user moves from one location to another across cells which could pose problems as each cell operates at a different frequencyIt is the process of automatically transferring the. This is done in GSM. Radiation patterns are available in different types like the following.
GSM Channel Links GSM BCCH Broadcast Control Channel GSM FCCH Frequency Correction Channel GSM SCH Synchronization Channel GSM RACH Random Access Channel GSM PCH Paging Channel GSM CCCH Common Control Channel GSM FACCH Fast Associated Control Channel GSM SACCH Slow. GSM divides the 25 MHz band into 124 channels each having 200 KHz width and remaining 200 KHz is left unused as a guard band to avoid interference. Time Division Multiple Access TDMA.
The Mobile Station MS The Base Station Subsystem BSS The Network Switching Subsystem NSS The Operation Support Subsystem OSS GSM - The Mobile Station. Different types of channels are as follows. GSM GSM has logical control and traffic channels.
Forward Traffic Channels are code channels used to assign call usually voice and signaling traffic to individual users. Access Channels are used by mobile stations to initiate communication with the. The Wireline channels are used for the transmission of voice as well as data information.
A Communication channel provides the connection between the transmitter and receiver. GSM is a circuit-switched system that divides each 200 kHz channel into eight 25 kHz time-slots. I BCCH ii CCCH iii DCCH.
These are main control channels in GSM. There are several forms of control channels in GSM and they can generally be divided into three categories according to the manner in which they are supported on the radio interface and the type of signalling information they carry. A GSM network comprises of many functional units.
A subjective test can be set up according to the criterion that 75 percent of the customers perceive the voice quality at a given CN as being good or excellent the top two levels among the five circuit-merit CM grades. GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communication. We generally classify the concept of interference into the following types depending on how the noise signal causes a disruptive modification in the message signal.
The distance between the uplink and downlink frequencies. The GSM network can be broadly divided into. Available narrow bandwidth in a frequency channel is shared with multiple users by.
Common Control Channels CCCH are used for signaling between a Base Station BTS and a mobile station MS. Control channels used to for. There are three types of logical channels.
The designing of field patterns can be done like a function of different fields. Each frame of 8 physical channels are multiplexed in the frequency domain. GSM Channel are divided into two types.
The traffic channes are intended to carry encoded speech or user data. It uses the combination of FDMA and TDMA. ModulationModulation is the process of sending a signal by changing the characteristics of a carrier frequency.
Traffic channels carry speech or data. Channel separationThe separation between adjacent carrier frequencies. In the US GSM operates in the bands 850 MHz and 1900 MHz.
It has following types. Where these bands were already allocated the 850 MHz and 1900 MHz bands were used instead for example in Canada and the United States. Types of GSM Frequency Division Multiple Access FDMA.
1 The simulator of this test must be adjusted for different mobile speeds. They are designed over a logarithmic scale. Broadcast Control Channel BCCH is used to broadcast for instance.
Types of Interference. This allocation is static and can not be changed. 10 213 Explain the following Control Channels in GSM.
The traffic channels are used. Different bursts are mapped to these channels uniquely as per GSM TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION 0502. It uses 4 different frequency bands of 850 MHz 900 MHz 1800 MHz and 1900 MHz.
Code Division Multiple Access CDMA. What are the different types of CCH in GSM. Traffic channels are intended to carry encoded speech and user data.
1Broadcast control channel 2Common control channel 3Dedicated control channel. Traffic channels and control channels. This article includes all the concepts of GSM architecture and how it works.
1011 The Subjective Test. 9 214 What are different protocols used in GSM. Hybrid Channel Allocation which is a combination of the first two methods.
GSM operates on the mobile communication bands 900 MHz and 1800 MHz in most parts of the world. In GSM this is 200 kHz. GSM is an open and digital cellular technology used for mobile communication.
Slot for user 1 Slot for user 2 Slot for user 3 Slot for user 5 Slot for user 7 Slot for user 8 Slot for user 4 Slot for user 6. Available spectrum bandwidth is split into equal bandwidths of voice channels. For efficient operation FCA systems typically allocate channels in a manner that maximizes frequency reuse.
Fixed Channel Allocation FCA systems allocate specific channels to specific cells. These channels use the pair of wires that carry the signal in the electrical form.

No comments for "Explain Different Types of Gsm Channels"
Post a Comment