Posterior Wall Mi Is Best Identified in Which Leads
Select the best correct answer A. Tap card to see definition.
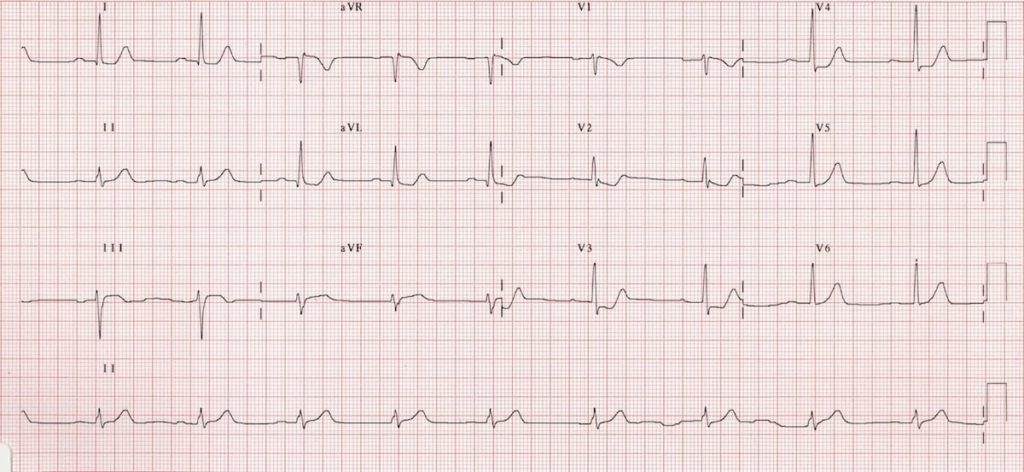
Posterior Myocardial Infarction Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
-EKG changes in lateral leads I aVL V5 and V6.

. A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in which leads. Patients typically have premature ventricular contractions and varying degrees of heart block. Posterior myocardial infarction MI represents 33 21 of all acute MIs and can be difficult to diagnose by the standard precordial leads.
However isolated posterior MI while less common 3-11 of infarcts 2 is important to recognize as it is also an indication for reperfusion and can be missed by the ECG reader. Luckily leads V1 V3 directly face the posterior wall of the left ventricle and are the mirror image of the posterior wall of the left ventricle. Interior wall MI is causes by occlusion of the right coronary arter and left circumflex.
Typically leads V7 V9 are needed to diagnose this entity. ____ ____ usually accompanies an anterior or inferior wall MI. Myocardial infarction is typically the result of a blockage in one of the coronary.
This occurs because these ECG leads will see the MI backwards. ST segment elevation in the posterior leads of a posterior ECG leads V7-V9. A posterior ECG is done by simply adding three extra precordial leads wrapping around the.
-Usually caused by blockage in left circumflex artery. The 2013 ACCFAHA STEMI guidelines suggest that ST depression in 2 or more leads of V1-4 may indicate transmural posterior injury and the AHAACC 2017 Clinical Performance and Quality Measures for Adults With ST-Elevation and NonST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction indicate that isolated PMI is a STEMI equivalent and should be treated. V4 and V5 B.
ArticleErdem2009DetectingPW titleDetecting posterior wall acute myocardial infarction by electrocardiogram authorAlim Erdem and Osman Can Yontar and Mehmet Birhan Yılmaz journalThe American journal of cardiology. Posterior wall MI is most commonly associated with an inferior or lateral STEMI occurring 15-20 percent of the time. Detecting posterior wall acute myocardial infarction by electrocardiogram.
The MAC Group does not replace the primary functions of EOCs or other dispatch organizations. Posterior wall is caused by the occlusion of the right coronary artery circumflex. Treatment for acute myocardial infarction in the prehospital environment may include all of the following EXCEPT _____.
A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in which leads. V7 Left posterior axillary line in the same horizontal plane as V6. V1 and V2 C.
A posterior wall myocardial. V8 Tip of the left scapula in the same horizontal plane as V6. Recent reports have demonstrated that artificial neural networks can be used to.
Automated interpretation of ECG is widely used as decision support for less experienced physicians. Leads V7-9 are placed on the posterior chest wall in the following positions see diagram below. ST segment depression not elevation in the septal and anterior precordial leads V1-V4.
1 and aVL D. -Reciprocal changes in V1 V2. An ECG performed with the use of posterior leads revealed ST-segment elevation in leads V 7 V 8 and V 9 which was consistent with posterior-wall myocardial infarction.
The mac group does not replace the primary functions of the EOC or other dispatch Weegy. The precordial ST-segment depressions are the mirror image. A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in V1 and V2.
Posterior wall ST-elevation myocardial infarction commonly occurs as a complication or extension of acute inferior wall STEMI. Incident Reports such as Situation Reports and Status Reports enhance situational awareness and ensure that personnel can access needed information. V9 Left paraspinal region in the same horizontal plane as V6.
Background The 12-lead ECG together with patient history and clinical findings remains the most important method for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Nitrous oxide A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in. A RS wave ratio greater than 1 in leads V1 or V2.
Anteroseptal infarction result form occlussion of the left anterior descending LAD 3. The ECG findings of an acute posterior wall MI include the following. A posterior wall myocardial infarction is best identified in which leads.
In this setting ST-segment depressions appear in the right precordial leads V1 V2 and V3 along with classic ST-segment elevations in the inferior leads. The leads are placed anteriorly but the myocardial injury is posterior. Lateral infarction is due to the occlusion.

Posterior Myocardial Infarction How Accurate Is The Flipped Ecg Trick
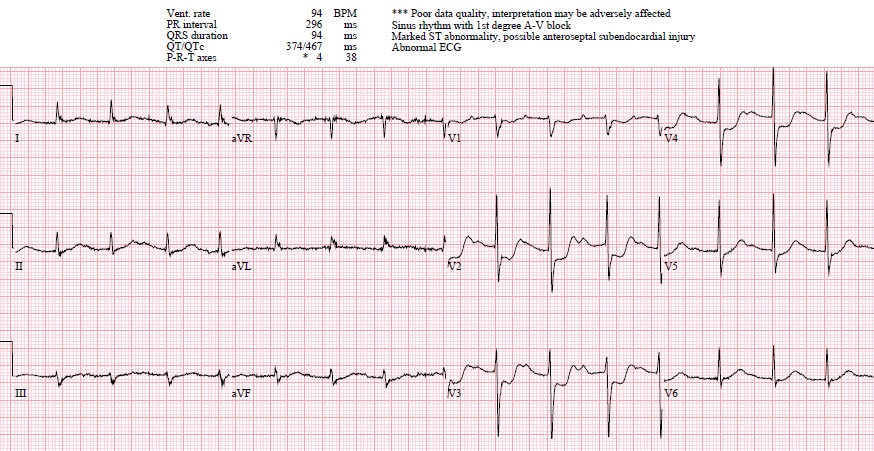
Posterior Mi Ecg Cases 6 Emergency Medicine Cases
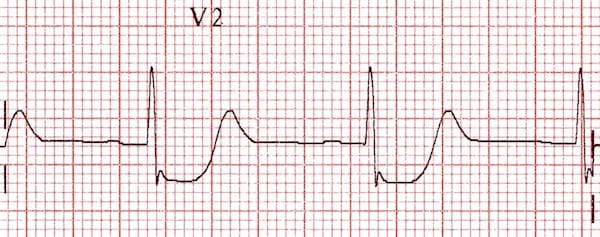
Posterior Myocardial Infarction Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis

Posterior Myocardial Infarction How Accurate Is The Flipped Ecg Trick
No comments for "Posterior Wall Mi Is Best Identified in Which Leads"
Post a Comment